There is no Royal Road to Geometry - Euclid
Recently, I was doing some ROS development and TF2 is a ROS package for tracking coordinate frames over time and affine transformation is essentail for understanding how it works.
In geometry, an affine transformation can be represented by acting a linear transformation and a translation on a vector.
Examples of affine transformation:
Transformation name
Affine matrix
Example
identity
[ 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
rotation
[ cos ( θ ) − sin ( θ ) 0 sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}\cos(\theta )&-\sin(\theta )&0\\\sin(\theta )&\cos(\theta )&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ cos ( θ ) sin ( θ ) 0 − sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) 0 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
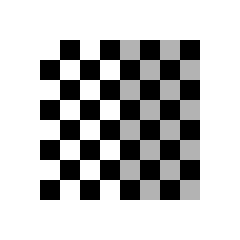
scaling
[ c x = 2 0 0 0 c y = 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}c_{x}=2&0&0\\0&c_{y}=1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ c x = 2 0 0 0 c y = 1 0 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
shearing
[ 1 c x = 0.5 0 c y = 0 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}1&c_{x}=0.5&0\\c_{y}=0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ 1 c y = 0 0 c x = 0 . 5 1 0 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
reflection
[ − 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ − 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
translation
[ 1 0 v x > 0 0 1 v y = 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}1&0&v_{x}>0\\0&1&v_{y}=0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ 1 0 0 0 1 0 v x > 0 v y = 0 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
“Affine Transformation” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 16 November 2021, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affine_transformation.
It can be represented with the following formula:
y ~ = A x + b . {\displaystyle \mathbf {\tilde y} =A\mathbf {x} +\mathbf {b} .}
y ~ = A x + b .
Which is a equivalent to the following matrix:
[ y 1 ] = [ A b 0 . . . 0 1 ] [ x 1 ] {\begin{bmatrix}y \\1 \end{bmatrix} = \left[\begin{array} {ccc|c} & A & & b \\ 0 & ... & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right] \begin{bmatrix}x \\1 \end{bmatrix}}
[ y 1 ] = [ 0 A . . . 0 b 1 ] [ x 1 ]
Code snippet:
affine_transformation.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 from __future__ import print_functionimport cv2 as cvimport numpy as npimport argparseparser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Code for Affine Transformations tutorial.' ) parser.add_argument('--input' , help ='Path to input image.' , default='src/MarioNSMBUDeluxe.png' ) args = parser.parse_args() src = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile(args.input )) if src is None : print ('Could not open or find the image:' , args.input ) exit(0 ) srcTri = np.array( [[0 , 0 ], [src.shape[1 ] - 1 , 0 ], [0 , src.shape[0 ] - 1 ]] ).astype(np.float32) dstTri = np.array( [[0 , src.shape[1 ]*0.33 ], [src.shape[1 ]*0.85 , src.shape[0 ]*0.25 ], [src.shape[1 ]*0.15 , src.shape[0 ]*0.7 ]] ).astype(np.float32) warp_mat = cv.getAffineTransform(srcTri, dstTri) warp_dst = cv.warpAffine(src, warp_mat, (src.shape[1 ], src.shape[0 ])) center = (warp_dst.shape[1 ]//2 , warp_dst.shape[0 ]//2 ) angle = -50 scale = 0.6 rot_mat = cv.getRotationMatrix2D( center, angle, scale ) warp_rotate_dst = cv.warpAffine(warp_dst, rot_mat, (warp_dst.shape[1 ], warp_dst.shape[0 ])) cv.imshow('Source image' , src) cv.imshow('Warp' , warp_dst) cv.imshow('Warp + Rotate' , warp_rotate_dst) cv.waitKey()
Calculation Example